Art50campus aims to provide a wide range of information and designed as a guide to readers from various disciplines who are interested in art, and enthusiastic to learn more. Various articles on the history of art, on major artists and artworks, art movements, themes in contemporary art as well as the most recent art agenda will be available to read for everyone.
‘From Renaissance to Contemporary Art’ is the section organized chronologically, in which you will find important periods in the western art history, starting from the 15th-century up until today. The main characteristics of specific art periods, styles, and major ideas are emphasized.
Renaissance (15-16. yy)
Renaissance means rebirth “Rinascimento” in Italian. It emerges with a gradual development of Humanism during the 14th-century and takes its source from Antiquity. It develops in Italy because of the economic growth in the country during the 15th century. Later, it spreads all over Europe. Renaissance is the beginning and appreciation of new world views and developments in the fields of literature, philosophy, science, art, and politics. It is the rebirth of ancient Greek and Roman Art and is considered as Europe’s awakening from centuries of sleep and pressure.
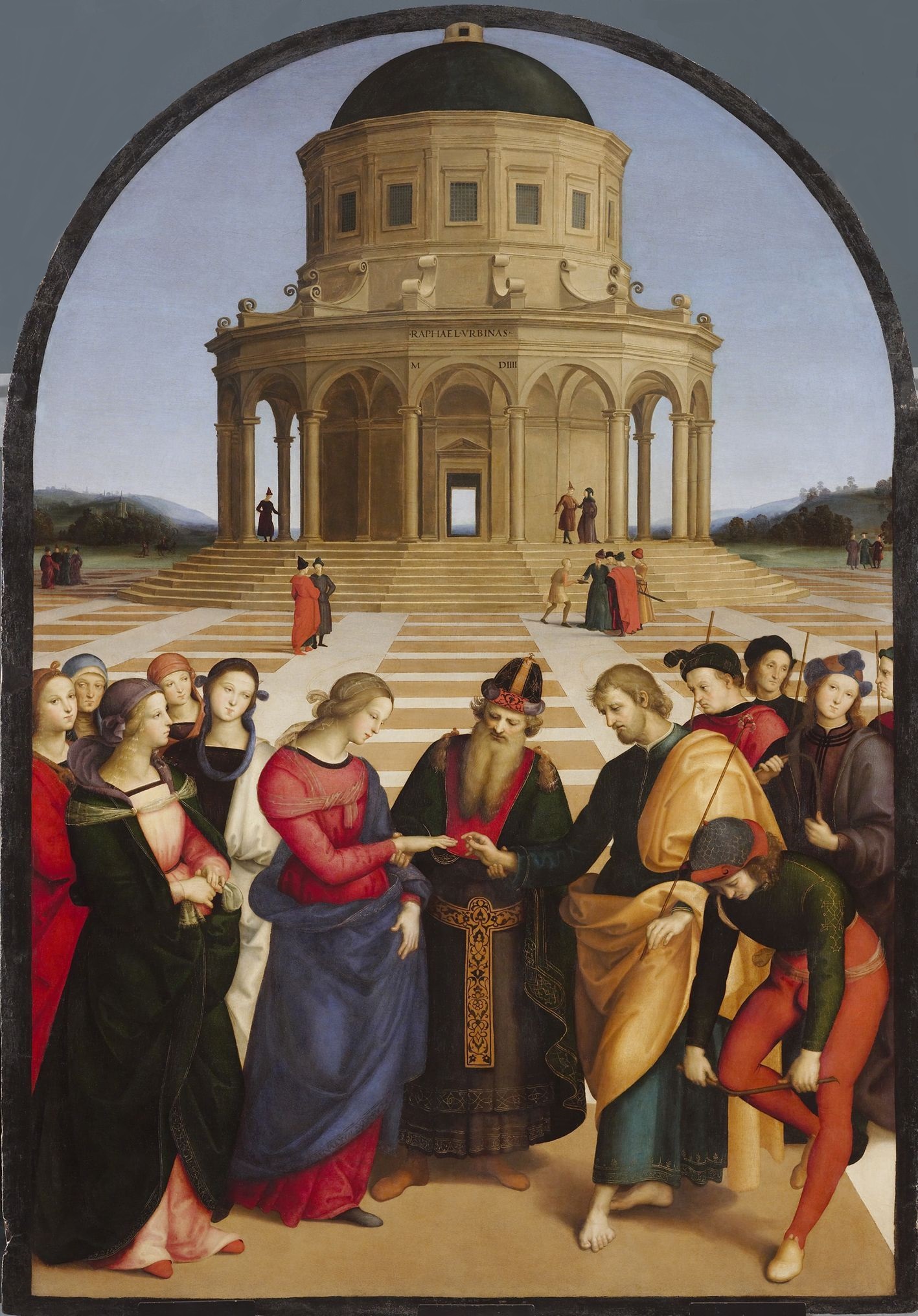

The Italian Renaissance is divided into three periods, namely; the Early Renaissance (from 1410 to the end of the 15th century), the High Renaissance (the first half of the 16th century), and the Late Renaissance (the second half of the 16th century to the 17th century).
The subjects in the Renaissance paintings are usually religious, historical events, and/or mythological. Also, ‘Nudity’ and portraiture become important throughout the paintings and sculptures. When the compositions are analyzed, the figures are mostly depicted on the foreground and the narration is made over these figures. The depiction of volumes, in other words, the three-dimensional illusion of nature and human bodies by using lighting and shading effects become important during the Renaissance. Artists use systematic methods to represent the world and they master these techniques of painting. Throughout their compositions with the use of ‘linear perspective’ to depict the illusion of reality, the paintings have the characteristics of symmetry, balance, and are in mathematical order.
Some of the renowned artists are; Rafaello Sanzio, Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo Buonarroti, Sandro Botticelli, Tiziano, Tintoretto, Masaccio, Bellini, Ghirlandaio and Verocchio in Italy. In France: Jean ve François Clouet, in Spain Fernando Yanez de Almedina, in Netherlands: Jan Van Eyck, Pieter Bruegel (Elder), Hieronymus Bosch and Albrecht Dürer in Germany.
Barocco (17-18. yy)
Derived from the word ‘Barocco’ in Portuguese, Baroque means ‘irregular, a pearl that is not precisely round,’ metaphorically, also defined as ‘strange, ridiculous, and incoherent’. In visual arts, ‘Baroque Age’ begins during the 17th century and continues until the end of the 18th century. The Baroque style evolves in Italy and then spreads throughout Europe.
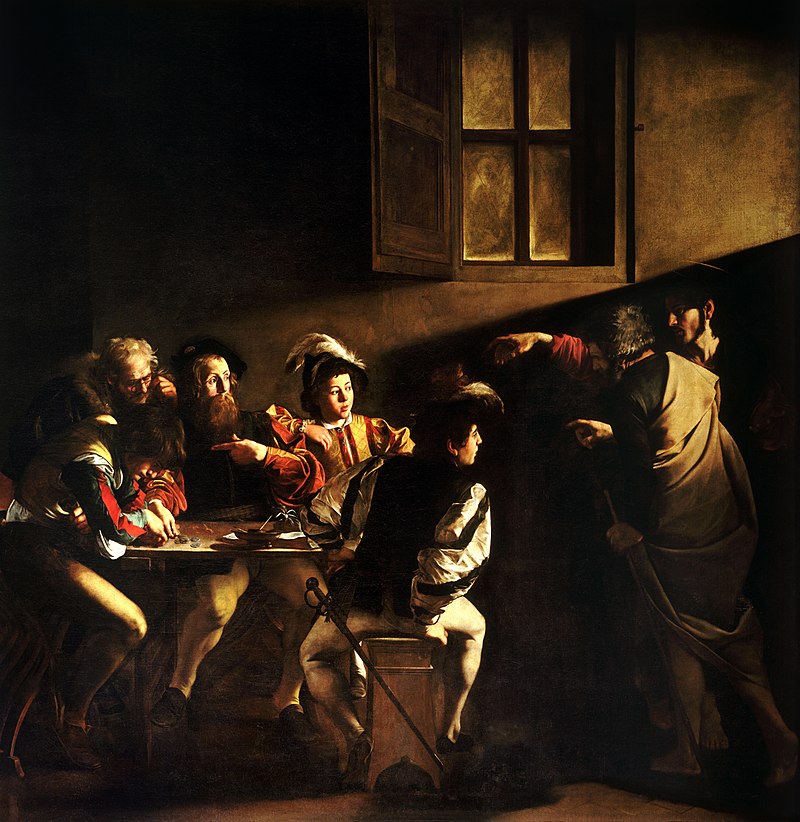

Baroque painters depict religious and mythological subjects, as well as scenes from daily life such as portraiture, landscape, and interiors. In their paintings, they focus on the use of dramatic light-shadow (chiaroscuro) effects in which the sense of depth is reinforced by the movement of the figures. The sculptures in the Baroque Period draw attention by their strong expressiveness in which the emotional intensity is exaggerated. Multi-figured sculptures force the viewer to walk around by reflecting a sense of mobility given by the light effects on the surfaces. A realistic expression is applied in theatrical arrangements.
Some of the renowned artists of the movement are; Michelangelo Merisi is also Caravaggio, Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Nicolas Poussin, Peter Paul Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, Johannas Vermeer and Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velazquez.
Rococo (18. yy)
Rococo, a style of decoration, emerges in France in the first half of the 18th century then spreads to Europe. The term ‘rococo’ is formed by the combination of two words: the rocaille meaning ‘pebble’ in French and the word Barocco. Rococo is an interior design and furniture style, but it also manifests itself in fine arts. The most striking feature is the evaluation of the paintings with the interior spaces by considering the size, shape, characteristics, and ornaments that will be used functionally together within the place where they will stand together. The use of pastel paints, asymmetrical compositions, use of curve-linear lines, volatility, and mobility draw attention throughout the Rococo paintings.

Some of the renowned artists are: Jean-Honore Fragonard, François Boucher and Jean-Antoine Watteau.
Neo-Classicism (18- 19. yy)
Neo-Classical movement initiates in Italy during the second half of the 18th century and spreads all over Europe. Neo-Classicism stands on the artistic styles of ancient Greek and Roman art. It evokes admiration for the art of antiquity against the excessive ornamentation and artificiality of Baroque and Rococo styles. Linearity and simplicity are quite visible in Neo-Classical paintings. The use of smoothly applied paint and explicit forms of expression can be traced. Based on the ‘noble simplicity and calm grandeur’ notion, the sculptures are created in calm positions and avoid reflecting any emotion or excitement.
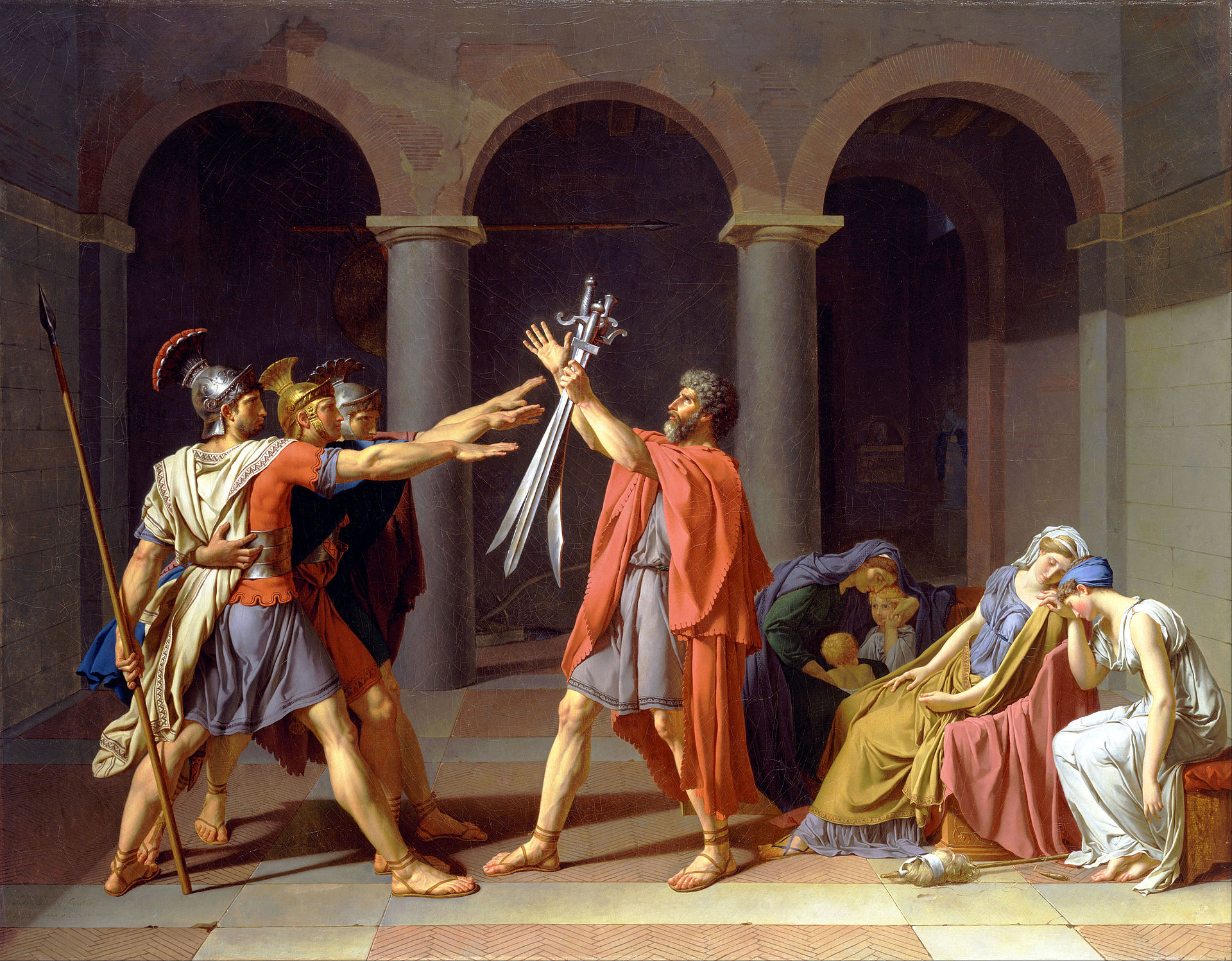

Some of the renowned artists are; Jacques-Louis David, Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres, Jean-Paul Laurens, and Joseph- Marie Vien.
Romanticism (18-19. yy)
Romanticism takes its name from the stories and myths told in the languages of Latin origin. It arises in response to Nationalism and the Neo-Classical movement that prevailed during the 18th century. Romanticism opposes everything that interferes with man’s freedom of creating. It spreads all over Europe, especially in England, Germany, and France. Irrationality, sensuality, excitement, instinct, freedom of expression, supernatural, love of nature, nationalism, escape to utopia, and many other concepts are associated with this movement within the political, social, economic events of the period.
In many paintings of this movement, the landscapes become popular in terms of the subject matters which previously, in art history, attributed as unimportant. The depicted scenes from nature, appeal to the intellectual power of the viewer as well as appealing to the emotions. And they lead the viewer to analyze and examine their mood and the emotions that the paintings arise.
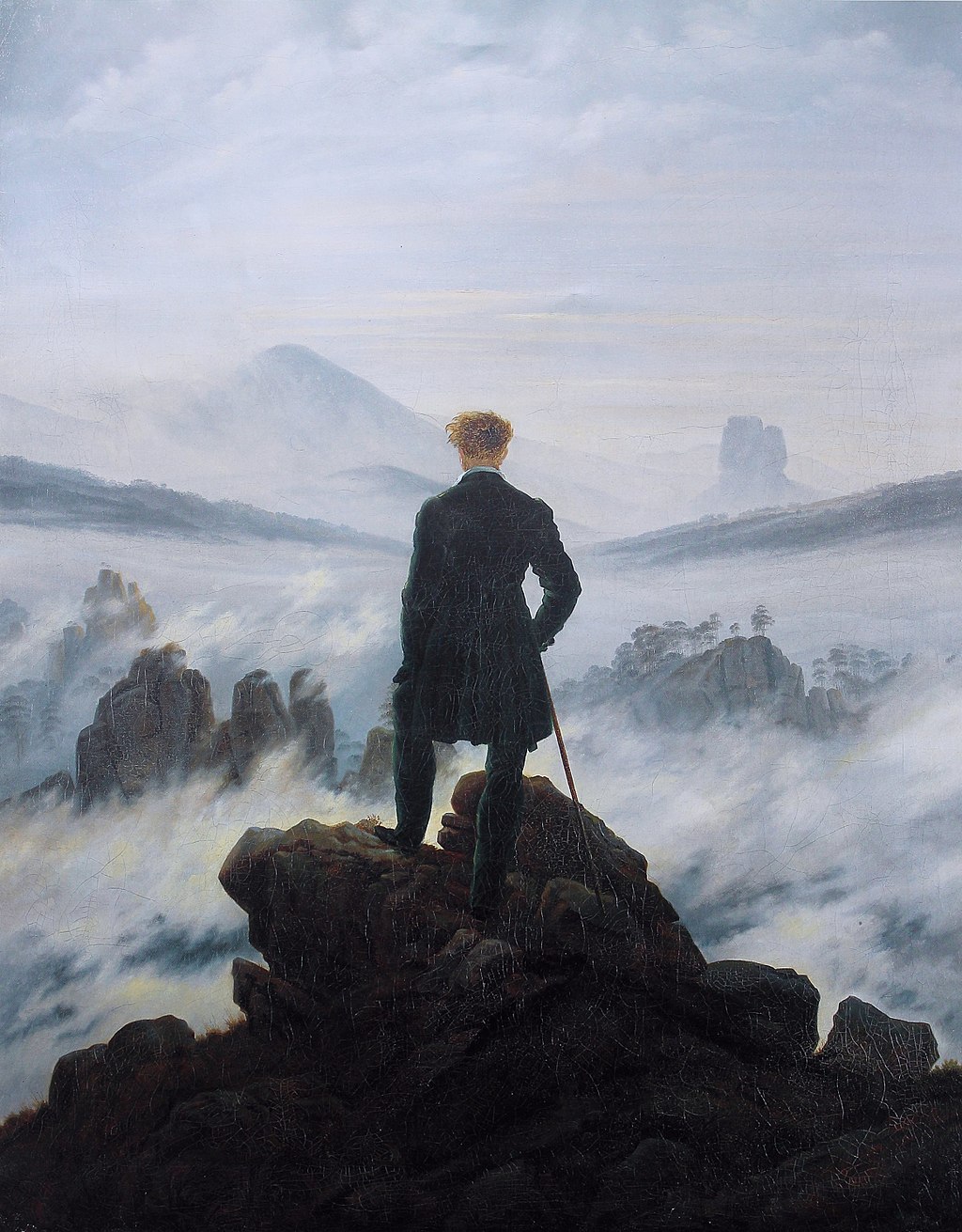

Some of the renowned artists of the period are: J.M.W. Turner, Caspar David Friedrich, John Constable and William Blake, Anton Koch.
Realism
Realism spreads in Europe during the mid-19th century as a concept in aesthetics and literature. With its orientation towards objectivity, it is an approach that stands against certain rules and styles applied in the arts up to that time. Realism defends that beauty and truth have a distinctive symptom at any time and under any circumstances. It is a consequence of industrialization, urbanization, and democratization in the West. In the paintings, the everyday lives of the poor, the peasants, the workers are depicted without representation of any emotion and glorification.
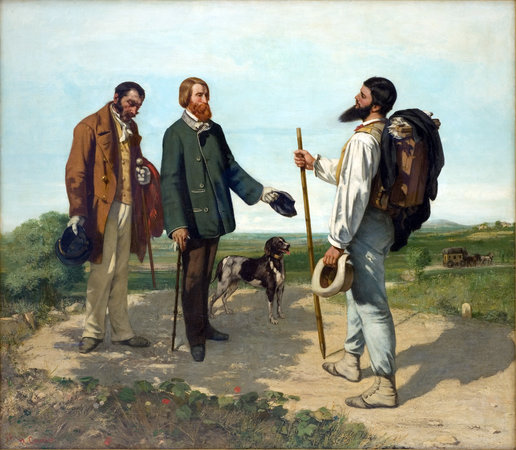

Resimlerde konu olarak yoksullar, köylüler, işçiler, ile günlük hayatın en basit gerçekleri duygusallığa yer vermeden ve yüceltilmeden betimlenir.
Some of the renowned artists are; Gustave Courbet, Jean Francois Millet, Jules Breton and Edouard Manet.
Impressionism
Impressionism is a movement that has greatly influenced the arts during the 20th-century. The Impressionist artists choose their subjects from daily lives, according to their personal preferences and depicted their paintings without applying the established rules. At the time, the widespread of photography, artists’ social environments, the influence of Japanese stamps, and modernization are the main elements that affected the subjects of the impressionist painters. Although the works of impressionist artists differ from each other in terms of their compositions and their styles, they convey contemporary life as the main subject.

The form, which has been accepted as the indispensable element in the paintings thus far, loses its importance with the Impressionists. Along with the artist’s efforts to reflect the nature, the concepts of light, color, changes in the atmosphere, and the instant, that exact moment, depicted based on the sensitivity of the eyes. The canvases, which were previously produced under artificial light inside studios, are carried into nature with the impressionists. In contrast to the black and dark tones used in the paintings, light and vibrant colors are used depending on the observations made outdoors under the natural light.
Some of the renowned artists are; Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, Camille Pissarro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley.
Post-Impressionism
Post-Impressionism emerges with a search for a new quest after Impressionism. Throughout the paintings of the Post-Impressionists, a more independent language of expression is used while depicting the colors, lights, and other compositional elements. Each artist has his/her unique style but common sense in terms of not applying the established rules of painting. Post-Impressionists take their subjects from daily lives and convey from their own perspectives of lives. They draw attention with thick contours, bright and vibrant colors, and expressive brushstrokes. The representation of emotions and the inner worlds of the artists also become more of an issue with this movement.
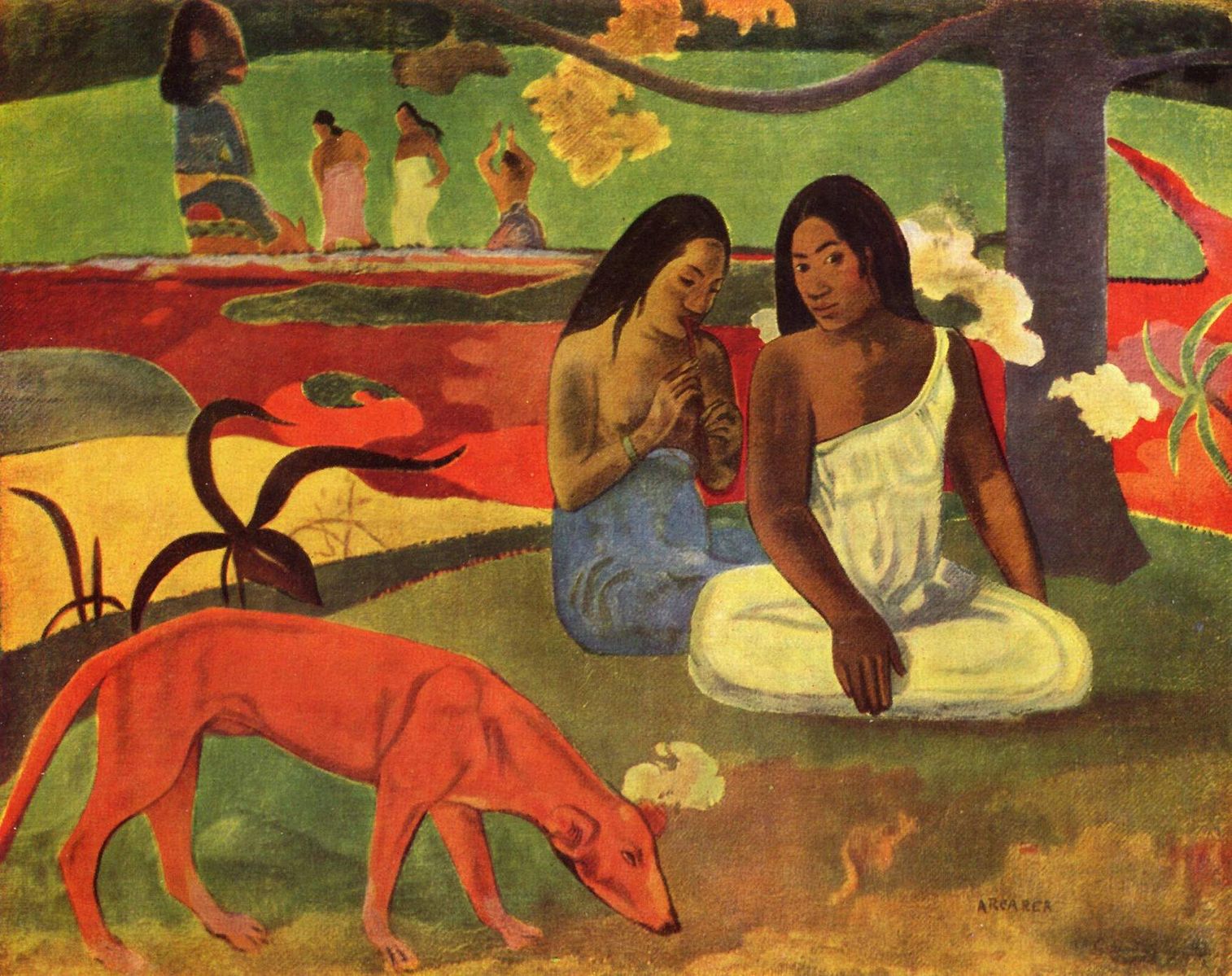

Some of the renowned artists are; Paul Cezanne, Vincent Van Gogh, Paul Gauguin and Toulouse Lautrec.
Dada
Dada emerged simultaneously in New York and Zurich in 1915-16. It is revealed by the gatherings of the artists who lost their faith for the future, caused by the trauma of the First World War, and felt despair and pessimist. Because of its destructive consequences, they believed that war is a result of the mindset of bourgeoise and the capitalist society. From this point of view, Dada eliminates the logic by dragging the ridiculous and meaningless where there is no rationality. It conveys the subconscious and in this way lays the foundations of the Surrealist movement. Dada emphasizes the pointlessness, uselessness, and nothingness of everything. With its anti-art stance, the artists oppose the traditional understandings of “art” and the perception of art that appeals to the eyes of the viewer. With Dada, new ways and mediums of expression emerge without any specific style or unity.
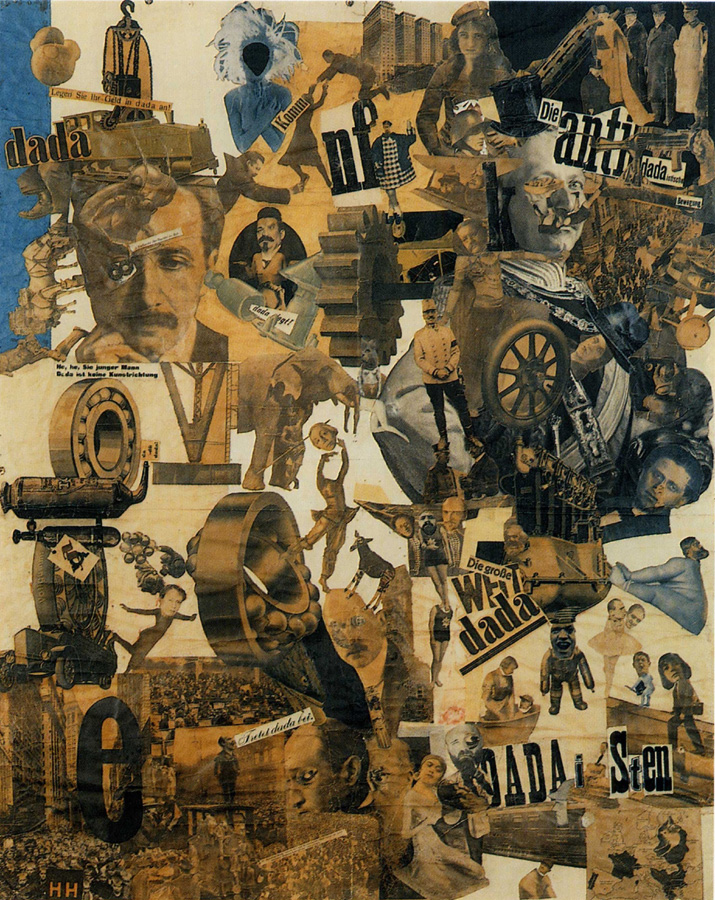

Some of the renowned artists are; Marcel Duchamp are Raoul Hausmann, Hannah Höch, Gerorge Grosz, Man Ray, Hans Arp and Francis Picabia.
Surrealism
Born out from the ashes of Dada, Surrealism defends creativity against Dada’s nihilistic attitude. Surrealists’ quest to reach the subconscious, dreams, apparent reality beyond the mind is all about examining the limits of a cultural and social structure that they think is morally demolished. The artists who believe that boundlessness and reality will be reached by destroying the logical order, they evaluate it by the depictions of the reason rather than the depictions of what is seen.
According to Surrealists, reaching the subconscious and a quest to arrive at the real source of desires and anxieties are the necessities of artistic creation. Surrealist artists adopt methods based entirely on randomness, they distorted the forms and placed found objects, used collage and frottage techniques as well as automatism and decalcomania. While creating their artworks the superiority of spontaneity becomes a dominant element.
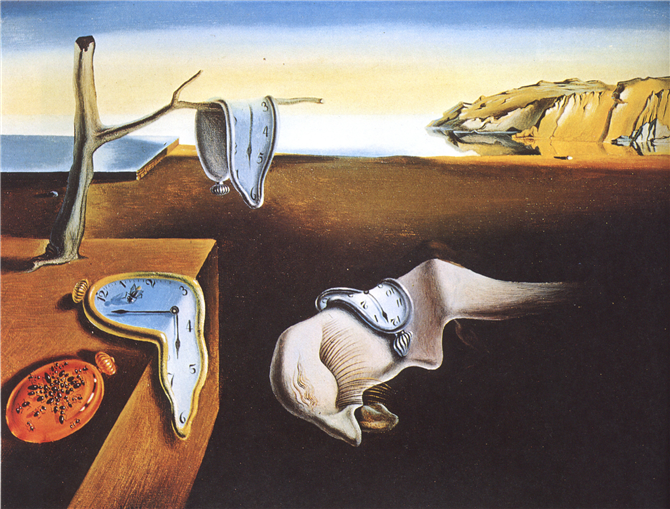
Some of the renowned artists are; Salvador Dali, Yves Tanguy, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst, Man Ray, Joan Miro, Andre Masson, Giorgio de Chirico and Arnold Böcklin.
Expressionism
Expressionism is a movement that emerges at the beginning of the 20th century in Europe, under a period in which the environment of uneasiness, astonishment, and a quest for change is dominant. Rather than copying the nature and figures as they are, it is the expression of the artist’s feelings and their inner worlds through the use of expressive colors, lines, and brushstrokes. The figures are represented subjectively by considering the influence and the emotion that they left on the artists.
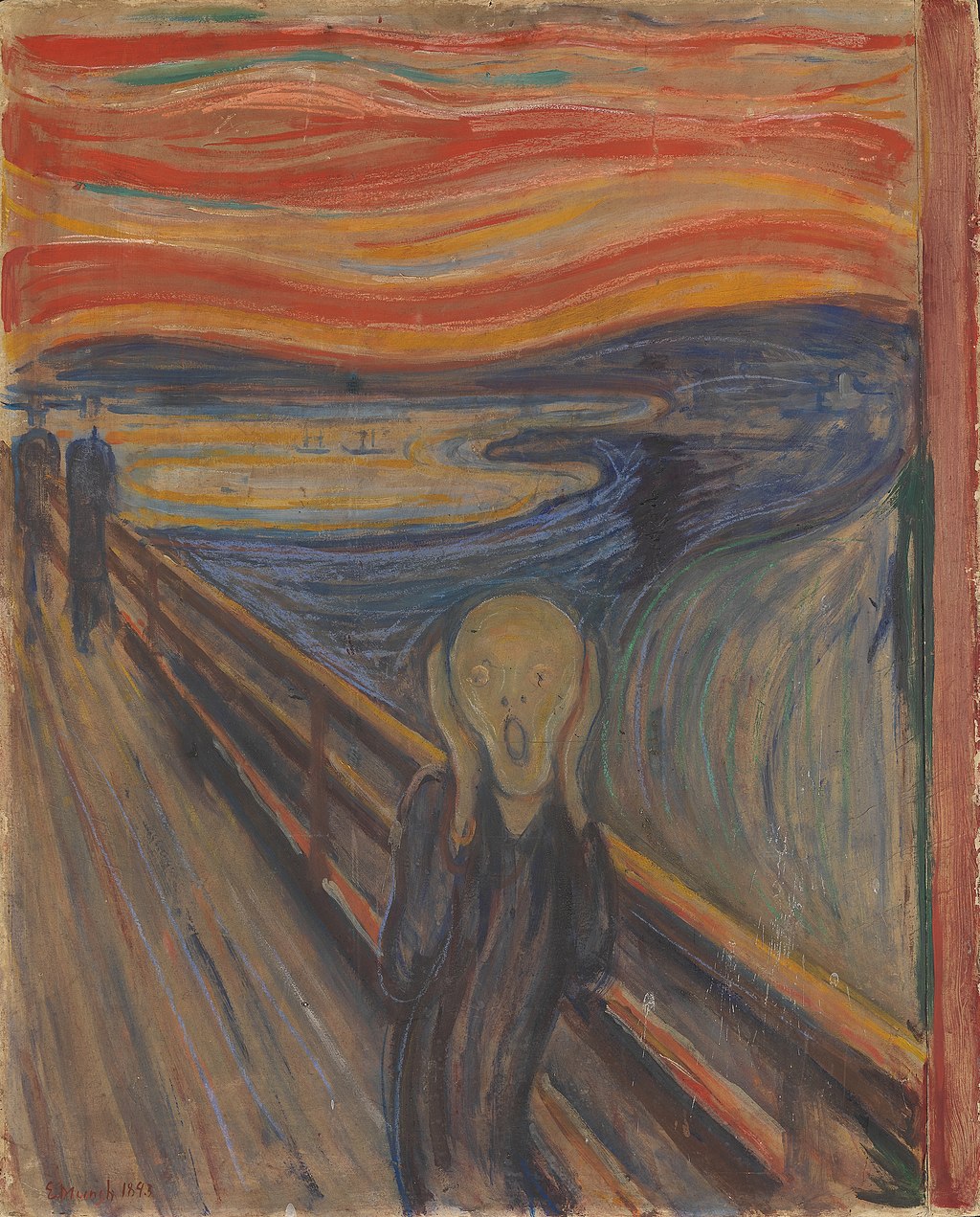

While depicting their compositions the artists deform the lines and figures, use unnaturalistic colors by adopting an expressive style. They rearrange and represent the world according to their aesthetic comprehensions by leaving the traditional canons of the painting.
Some of the renowned artists are; Edvard Munch, Max Beckmann, Erick Heckel, Egon Schiele, Oskar Kokoschka, Ernst Ludwing Kirchner, Franz Marc, Emil Nolde, and Aguste Macke.
Cubism
Cubism emerges in 1907-08 with the pioneering of Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. Cubist paintings create a new language by focusing on the lines and forms and using color as a secondary element. It is a movement that offers a new way of seeing and representing the world. Cubism demolishes the tradition of perspective which is used for many centuries, by questioning the notion to create a pictorial space without using it and becomes one of the most radical art movements of the 20th century. Reflecting on a conceptual interpretation of nature rather than descriptive, Cubist artists emphasize the two-dimensionality of the painting surface instead of creating an illusion of three-dimensionality and simultaneously represent the fourth dimension by displaying the objects from multiple viewpoints.

Cubism is divided into two as; Analytical Cubism and Synthetic Cubism. In Analytic Cubism, forms are fragmented into facades and are depicted in their simplest forms, while monochrome colors are used. The foreground and the background of the paintings are intertwined and the facades create integrity. In Synthetic Cubism, different materials are added onto the surface of the canvases. Using everyday materials such as newspapers, pieces of wallpapers, and applying the collage technique which is gluing the objects onto the surface of the canvas, they reach the whole.
Some of the renowned artists are; Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, Juan Gris, Fernand Leger, Jean Metzinger, and Albert Gleizes.
Abstract Art
Abstract art is the gathering of the arrangements of geometric or amorphous forms that do not mimic reality. It can be entirely a depiction of a dream, it can be a representation of abstracted forms or/and redefinition of figures or an object in nature without carrying any similarities. Abstract paintings can be divided into two; mental, structural, and geometric; and instinctive, emotional, and decorative. In abstract paintings, the compositions are drawn according to the subjectivity of the artists, in which the forms, colors, and figures do not mimic reality or may not be related at all. At the beginnings of some of the processes of the artists in abstract art, the artist examines the nature and abstracts the forms, figures. But in the end, remains no similarity between nature and the artwork.
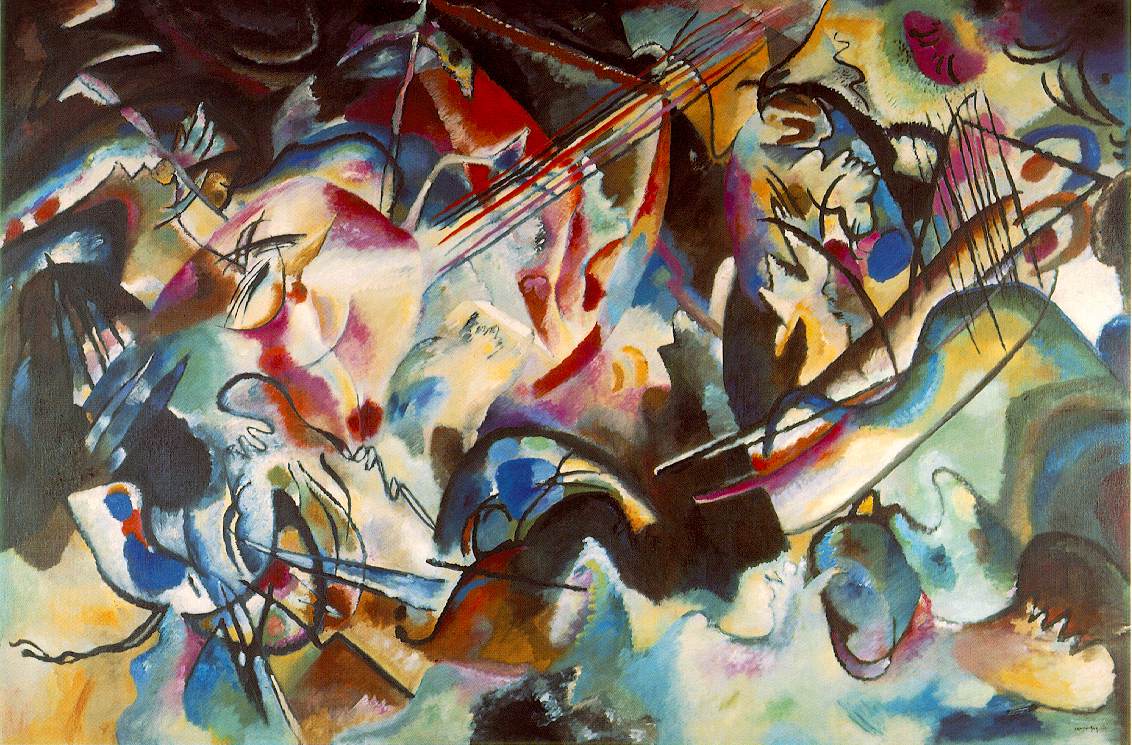
Some of the renowned artists are; Vassily Kandinsky, Kazimir Malevich, Sonia Delounay, Naum Gabo.
Pop Art
Pop Art is an art movement that emerged independently from each other in England and then in the USA in the 1950s and 60s. Pop artists eliminate the distinctions between the ‘high culture’ aimed at the taste of an elite. By using readymade images from the consumer culture they turn these objects and images into sculptures or represent them on two-dimensional surfaces of the canvases. These objects include a wide variety of advertisements, food, and beverage materials, from Coca Cola bottles to cans, packs of cigarettes to hamburgers, the ordinary objects of everyday life of the American consumer society raised with new meanings in an artistic context. One of the most important features of Pop Art is its bonds with the audience. After the movements of Dada, Abstract Art, Abstract Expressionism the gap between the art and spectator has risen out, but with Pop, they got closer because of the use of familiar images from the consumer society.
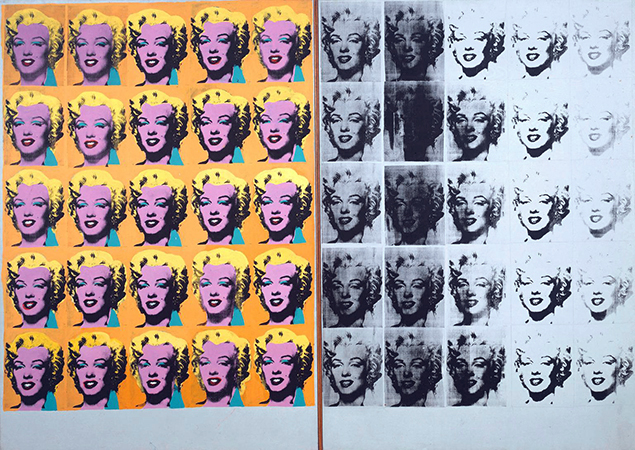

Some of the renowned artists are; Andy Warhol, Richard Hamilton, Robert Rauschenberg, Roy Lichtenstein, Claes Oldenburg and George Segal.
Sena Arcak Bağcılar
Sources:
Ahu Antmen, 20. Yüzyıl Batı Sanatında Akımlar, Yem Yayınları
Eczacıbaşı Sanat Ansiklopedisi, Yem Yayınları
Gardners Art Through Ages, Fred S. Kleiner and Richard Tansley, 10. Baskı
Art Since 1900, Modernism, Anti Modernism, Post Modernism, Foster, Hal et. all, Thames & Hudson

 Türkçe
Türkçe